Potentially Life-Threatening Injuries
These injuries still require serious consideration, in a player sustaining serious chest trauma.
Simple Pneumothorax
- Air leak into the pleural cavity, but there is no one way valve and so this does not “tension”
- Reduced air entry and hyper-resonant percussion note on affected side.
- Differs from tension pneumothorax in the clinical state of the patient. Those with a simple pneumothorax may be in pain and short of breath, but do not present with the profound distress and compromise of those with a tension pneumothorax
- ABCDE
- Oxygen
- Transfer to the Emergency Department as soon as possible
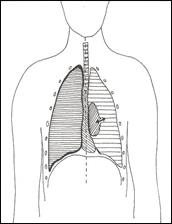
Pictorial representation of a simple pneumothorax
Haemothorax
- Blood in the thoracic cavity pleural space
- Usually in association with a chest wall injury
- Reduced air entry and stoney dull percussion note on the affected side
- Not as compromised, either respiratory or haemodynamically, as a massive haemothorax
- ABCDE
- Oxygen
- Transfer to the Emergency Department as soon as possible
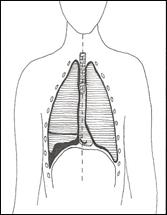
Pictorial representation of a haemothorax
Pulmonary Contusion
- Complex process of lung injury which in simple terms can be considered as bruising of the lung tissue
- Not immediately apparent and a high index of suspicion is important based on the mechanism of injury
- Care should be taken with fluid resuscitation and guidelines used for fluid resuscitation should be stringently applied
- ABCDE
- Oxygen
- Transfer to the Emergency Department as soon as possible
Tracheal Injury
- It is easy to overlook this injury during the initial assessment, particularly if there is no airway compromise
- It may present as subcutaneous emphysema across the anterior neck, haemoptysis, laryngeal tenderness, hoarseness or pain in the anterior neck region
- ABCDE
- Oxygen
- Transfer to the Emergency Department as soon as possible
Traumatic Aortic Rupture
- Due to rapid acceleration or deceleration injury.
- Rupture usually occurs at the ligamentum arteriosum, as the aorta is relatively fixed here compared to the rest of the relatively mobile aorta
- ABCDE
- Oxygen
- Transfer to an Emergency Department as soon as possible
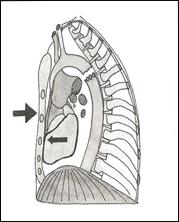
Pictorial representation of aortic rupture
Traumatic Diaphragmatic Rupture
- Most diagnosed on the left as the liver confers some protection on the right.
- May hear bowel sounds in the chest
- ABCDE
- Oxygen
- Transfer to an Emergency Department as soon as possible
Mediastinal Traversing Wounds
- These can be rapidly fatal and can cause a number of serious thoracic injuries. These can be identified as already outlined in this chapter.
- ABCDE
- Oxygen
- Specific treatment for identified injuries.
- Transfer to the Emergency Department as soon as possible